Custom cells and reading cells from STL¶
HemoCell provides different cell types to be used in the simulations. Most commonly, the red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets (PLTs) are used, often together in the same simulation. However, for different use-cases, we support changing the shapes and properties of these cells and even provide support for directly loading in cell geometries from STL files.
Details on the various configuration settings can be found here: configuration.
Specifying cell types¶
Usually cells are generated mathematically, i.e. the vertex locations and the
resulting triangulation are gathered from describing equations. In these cases,
the equations describe the shape of the resulting cells, allowing for RBCs by
RBC_FROM_SPHERE, platelets by ELLIPSOID_FROM_SPHERE, and WBCs by
WBC_SPHERE. These are then combined with a desired material model using the
hemocell.addCellType<M>(name, S) with M a material model and S the
desired shape. For instance, typical RBCs are specified as
hemocell.addCellType<RbcHighOrderModel>("RBC", RBC_FROM_SPHERE);
Reading cells from STL¶
Alternatively, cells can be loaded from STL directly. In that case, we change
the desired shape argument S to MESH_FROM_STL indicating that we want to
read the shape from an STL file. The path to this file should be given in the
corresponding CELL.xml file, where CELL is to be replaced with the used
string identifier for the cell type. The path should be provided in the
<hemocell><MaterialModel><StlFile> tag of the configuration file.
Note
The specification of a custom shape can still be combined with typical material models, however, care has to be taken that this combination still makes sense physically. For more advanced use-cases, one might consider to implement a correpsonding material model as well.
Note
The current STL reader only supports STL files written in ASCII format. Most software migth nowadays write STL using a binary format by default, so care should be taken to provide the STL file in ASCII format.
Cell shapes example¶
The example in examples/cell_shapes presents a small overview of different
type of cell types embedded in a small cubic domain, where the main file,
examples/cell_shapes/cell_shapes.cpp illustrates the initialisation of each
cell.
We consider four different cell types:
Standard, healthy red blood cells
hemocell.addCellType<RbcHighOrderModel>("RBC_HO", RBC_FROM_SPHERE);
Platelets using different levels of mesh refinement. The refinement level has been specific in
PLT.xmlusing the<hemocell><materialModel><minNumTriangles>configuration parameter.hemocell.addCellType<PltSimpleModel>("PLT", ELLIPSOID_FROM_SPHERE); hemocell.addCellType<PltSimpleModel>("PLT_HO", ELLIPSOID_FROM_SPHERE);
White blood (spherical) cells
hemocell.addCellType<WbcHighOrderModel>("WBC_HO", WBC_SPHERE);
Deformed red blood cells, read from STL. These load the geometry of the RBC directly from STL representing late-stage Malaria invested RBC models.
hemocell.addCellType<WbcHighOrderModel>("RBC_FROM_STL", MESH_FROM_STL);
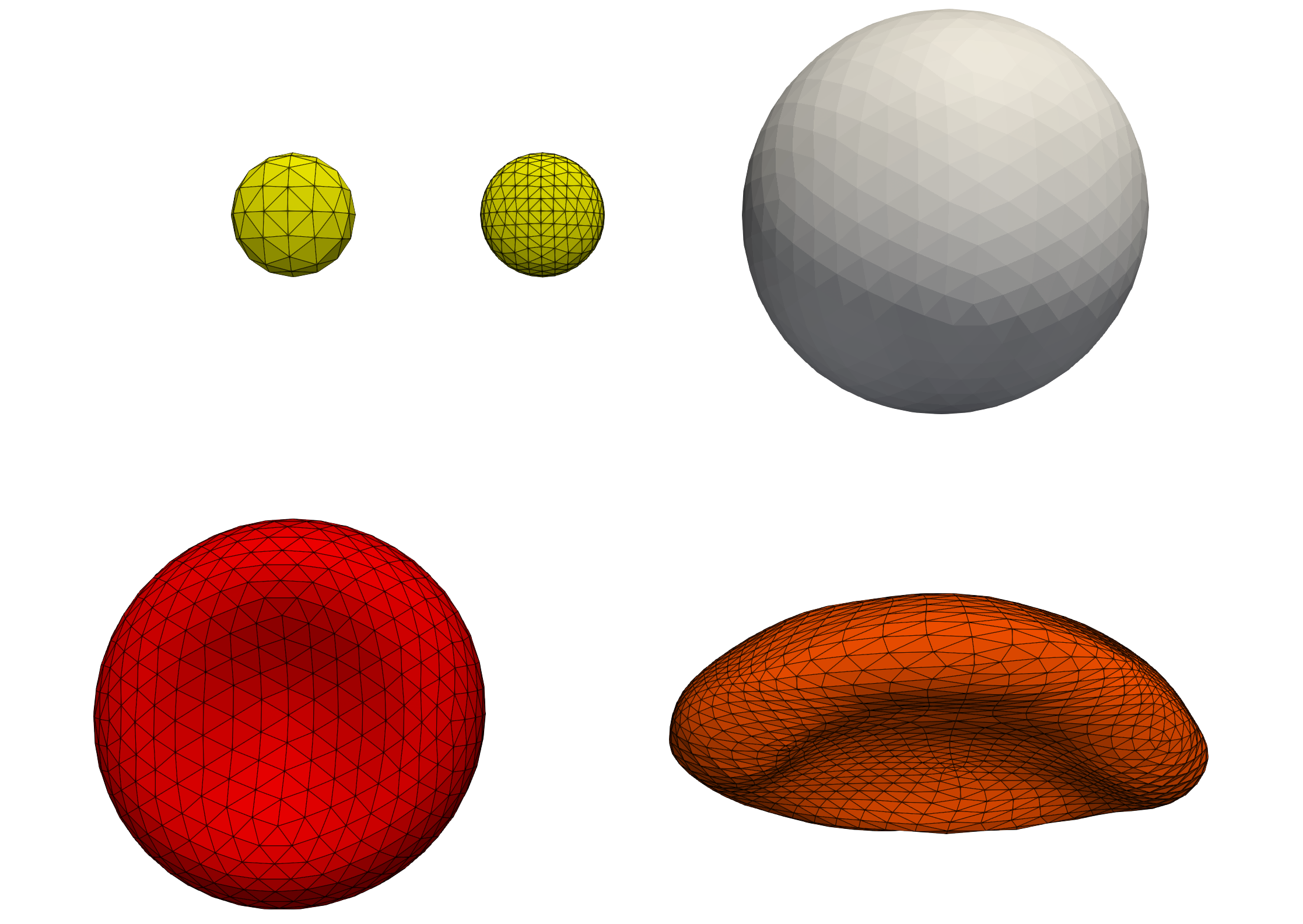
Illustration of different cell types supported in HemoCell. The yellow cells represent two platelets with a different number of minimum triangles used. The left discretisation uses less triangles, resulting in a less accurate but more performant surface representation. The white sphere corresponds to the white blood cell. The red cell to a healthy, “standard” shaped red blood cell. The orange cell corresponds to a cell geometry directly loaded through STL, representing a red blood cell to model a late-stage Malaria invested red blood cell.¶
